mirror of
https://github.com/massbug/judge4c.git
synced 2025-05-17 23:12:23 +00:00
1061 lines
29 KiB
TypeScript
1061 lines
29 KiB
TypeScript
import { PrismaClient, Prisma, EditorLanguage, LanguageServerProtocol } from "@/generated/client";
|
||
|
||
const prisma = new PrismaClient();
|
||
|
||
const editorLanguageConfigData: Prisma.EditorLanguageConfigCreateInput[] = [
|
||
{
|
||
language: EditorLanguage.c,
|
||
label: "C",
|
||
fileName: "main",
|
||
fileExtension: ".c",
|
||
languageServerConfig: {
|
||
create: {
|
||
protocol: LanguageServerProtocol.ws,
|
||
hostname: "localhost",
|
||
port: 4594,
|
||
path: "/clangd",
|
||
},
|
||
},
|
||
dockerConfig: {
|
||
create: {
|
||
image: "gcc",
|
||
tag: "latest",
|
||
workingDir: "/src",
|
||
compileOutputLimit: 1 * 1024 * 1024,
|
||
runOutputLimit: 1 * 1024 * 1024,
|
||
},
|
||
},
|
||
},
|
||
{
|
||
language: EditorLanguage.cpp,
|
||
label: "C++",
|
||
fileName: "main",
|
||
fileExtension: ".cpp",
|
||
languageServerConfig: {
|
||
create: {
|
||
protocol: LanguageServerProtocol.ws,
|
||
hostname: "localhost",
|
||
port: 4595,
|
||
path: "/clangd",
|
||
},
|
||
},
|
||
dockerConfig: {
|
||
create: {
|
||
image: "gcc",
|
||
tag: "latest",
|
||
workingDir: "/src",
|
||
compileOutputLimit: 1 * 1024 * 1024,
|
||
runOutputLimit: 1 * 1024 * 1024,
|
||
},
|
||
},
|
||
},
|
||
];
|
||
|
||
const userData: Prisma.UserCreateInput[] = [
|
||
{
|
||
name: "cfngc4594",
|
||
email: "cfngc4594@gmail.com",
|
||
password: "$2b$10$edWXpq2TOiiGQkPOXWKGlO4EKnp2YyV7OoS2qqk/W0E6GyiVQIC66",
|
||
role: "ADMIN",
|
||
problems: {
|
||
create: [
|
||
{
|
||
displayId: 1000,
|
||
title: "两数之和",
|
||
description: `给定一个整数数组 \`nums\` 和一个整数目标值 \`target\`,请你在该数组中找出 **和为目标值** _\`target\`_ 的那 **两个** 整数,并返回它们的数组下标。
|
||
|
||
你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案,并且你不能使用两次相同的元素。
|
||
|
||
你可以按任意顺序返回答案。
|
||
|
||
### 示例 1:
|
||
|
||
\`\`\`shell
|
||
输入:nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9
|
||
输出:[0,1]
|
||
解释:因为 nums[0] + nums[1] == 9 ,返回 [0, 1] 。
|
||
\`\`\`
|
||
|
||
### 示例 2:
|
||
|
||
\`\`\`shell
|
||
输入:nums = [3,2,4], target = 6
|
||
输出:[1,2]
|
||
\`\`\`
|
||
|
||
### 示例 3:
|
||
|
||
\`\`\`shell
|
||
输入:nums = [3,3], target = 6
|
||
输出:[0,1]
|
||
\`\`\`
|
||
|
||
## 提示:
|
||
|
||
\`\`\`math
|
||
2 <= nums.length <= 10^4
|
||
\`\`\`
|
||
\`\`\`math
|
||
-10^9 <= nums[i] <= 10^9
|
||
\`\`\`
|
||
\`\`\`math
|
||
-10^9 <= target <= 10^9
|
||
\`\`\`
|
||
|
||
<div align="center">
|
||
只会存在一个有效答案*
|
||
</div>
|
||
|
||
**进阶:** 你可以想出一个时间复杂度小于 \`O(n^2)\` 的算法吗?
|
||
|
||
---
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
\`\`\`C++
|
||
\`\`\``,
|
||
solution: `<VideoEmbed platform="youtube" id="tSI98g3PDyE" />
|
||
|
||
## 方法一:暴力枚举
|
||
|
||
### 思路及算法
|
||
|
||
最容易想到的方法是枚举数组中的每一个数 x,寻找数组中是否存在 target - x。
|
||
|
||
当我们使用遍历整个数组的方式寻找 target - x 时,需要注意到每一个位于 x 之前的元素都已经和 x 匹配过,因此不需要再进行匹配。而每一个元素不能被使用两次,所以我们只需要在 x 后面的元素中寻找 target - x。
|
||
|
||
|
||
### 代码
|
||
|
||
\`\`\`c showLineNumbers
|
||
int* twoSum(int* nums, int numsSize, int target, int* returnSize) {
|
||
struct hashTable {
|
||
int key;
|
||
int value;
|
||
UT_hash_handle hh;
|
||
} *hashTable = NULL, *item, *tmpItem;
|
||
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++) {
|
||
HASH_FIND_INT(hashTable, &nums[i], item);
|
||
if (item) {
|
||
int* result = malloc(sizeof(int) * 2);
|
||
result[0] = item->value;
|
||
result[1] = i;
|
||
*returnSize = 2;
|
||
HASH_ITER(hh, hashTable, item, tmpItem) {
|
||
HASH_DEL(hashTable, item);
|
||
free(item);
|
||
}
|
||
return result;
|
||
}
|
||
item = malloc(sizeof(struct hashTable));
|
||
item->key = target - nums[i];
|
||
item->value = i;
|
||
HASH_ADD_INT(hashTable, key, item);
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
HASH_ITER(hh, hashTable, item, tmpItem) {
|
||
HASH_DEL(hashTable, item);
|
||
free(item);
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
*returnSize = 0;
|
||
// If no valid pair is found, return an empty array
|
||
return malloc(sizeof(int) * 0);
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
\`\`\`
|
||
|
||
### 复杂度分析
|
||
|
||
- **时间复杂度:** $O(n^2)$.
|
||
|
||
其中 $n$ 是数组中的元素数量。最坏情况下数组中任意两个数都要被匹配一次。
|
||
|
||
- **空间复杂度:** $O(1)$.
|
||
|
||
所需的空间不取决于 input 数组的大小,因此仅使用恒定空间。
|
||
|
||
---
|
||
|
||
## 方法二:哈希表
|
||
|
||
### 思路及算法
|
||
|
||
注意到方法一的时间复杂度较高的原因是寻找 target - x 的时间复杂度过高。因此,我们需要一种更优秀的方法,能够快速寻找数组中是否存在目标元素。如果存在,我们需要找出它的索引。
|
||
|
||
使用哈希表,可以将寻找 target - x 的时间复杂度降低到从 $O(N)$ 降低到 $O(1)$。
|
||
|
||
这样我们创建一个哈希表,对于每一个 x,我们首先查询哈希表中是否存在 target - x,然后将 x 插入到哈希表中,即可保证不会让 x 和自己匹配。
|
||
|
||
### 代码
|
||
|
||
\`\`\`c showLineNumbers
|
||
int* twoSum(int* nums, int numsSize, int target, int* returnSize) {
|
||
struct hashTable {
|
||
int key;
|
||
int value;
|
||
UT_hash_handle hh;
|
||
} *hashTable = NULL, *item, *tmpItem;
|
||
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++) {
|
||
HASH_FIND_INT(hashTable, &nums[i], item);
|
||
if (item) {
|
||
int* result = malloc(sizeof(int) * 2);
|
||
result[0] = item->value;
|
||
result[1] = i;
|
||
*returnSize = 2;
|
||
HASH_ITER(hh, hashTable, item, tmpItem) {
|
||
HASH_DEL(hashTable, item);
|
||
free(item);
|
||
}
|
||
return result;
|
||
}
|
||
item = malloc(sizeof(struct hashTable));
|
||
item->key = target - nums[i];
|
||
item->value = i;
|
||
HASH_ADD_INT(hashTable, key, item);
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
HASH_ITER(hh, hashTable, item, tmpItem) {
|
||
HASH_DEL(hashTable, item);
|
||
free(item);
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
*returnSize = 0;
|
||
// If no valid pair is found, return an empty array
|
||
return malloc(sizeof(int) * 0);
|
||
}
|
||
\`\`\`
|
||
|
||
### 复杂度分析
|
||
|
||
- **时间复杂度:** $O(n)$.
|
||
|
||
其中 $N$ 是数组中的元素数量。对于每一个元素 x,我们可以 $O(1)$ 地寻找 target - x。
|
||
|
||
- **空间复杂度:** $O(n)$.
|
||
|
||
其中 $N$ 是数组中的元素数量。主要为哈希表的开销。
|
||
`,
|
||
difficulty: "EASY",
|
||
published: true,
|
||
templates: {
|
||
create: [
|
||
{
|
||
language: "c",
|
||
template: `
|
||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||
#include <string.h>
|
||
|
||
int *parseIntArray(char *line, int *len) {
|
||
line[strcspn(line, "\\n")] = 0;
|
||
char *p = line;
|
||
while (*p && (*p == '[' || *p == ' ' || *p == ']'))
|
||
p++;
|
||
|
||
int capacity = 10;
|
||
int *arr = malloc(capacity * sizeof(int));
|
||
*len = 0;
|
||
|
||
char *token = strtok(p, ",");
|
||
while (token) {
|
||
if (*len >= capacity) {
|
||
capacity *= 2;
|
||
arr = realloc(arr, capacity * sizeof(int));
|
||
}
|
||
arr[(*len)++] = atoi(token);
|
||
token = strtok(NULL, ",");
|
||
}
|
||
return arr;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
char *formatOutput(int *res, int resLen) {
|
||
if (resLen == 0)
|
||
return "[]";
|
||
|
||
char *buf = malloc(resLen * 12 + 3);
|
||
char *p = buf;
|
||
*p++ = '[';
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < resLen; i++) {
|
||
p += sprintf(p, "%d", res[i]);
|
||
if (i != resLen - 1)
|
||
*p++ = ',';
|
||
}
|
||
*p++ = ']';
|
||
*p = 0;
|
||
return buf;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
int *twoSum(int *nums, int numsSize, int target, int *returnSize);
|
||
|
||
int main() {
|
||
char line[1024];
|
||
while (fgets(line, sizeof(line), stdin)) {
|
||
int numsSize;
|
||
int *nums = parseIntArray(line, &numsSize);
|
||
|
||
if (!fgets(line, sizeof(line), stdin))
|
||
break;
|
||
int target = atoi(line);
|
||
|
||
int returnSize;
|
||
int *res = twoSum(nums, numsSize, target, &returnSize);
|
||
|
||
char *output = formatOutput(res, returnSize);
|
||
printf("%s\\n", output);
|
||
|
||
free(nums);
|
||
if (returnSize > 0)
|
||
free(res);
|
||
if (returnSize > 0)
|
||
free(output);
|
||
}
|
||
return 0;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
/**
|
||
* Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
|
||
*/
|
||
int* twoSum(int* nums, int numsSize, int target, int* returnSize) {
|
||
|
||
}`,
|
||
},
|
||
{
|
||
language: "cpp",
|
||
template: `
|
||
#include <iostream>
|
||
#include <vector>
|
||
#include <string>
|
||
#include <sstream>
|
||
#include <algorithm>
|
||
#include <unordered_map>
|
||
|
||
using namespace std;
|
||
|
||
// 解析输入字符串为整数数组
|
||
vector<int> parseIntArray(string line) {
|
||
vector<int> result;
|
||
line.erase(remove(line.begin(), line.end(), '['), line.end());
|
||
line.erase(remove(line.begin(), line.end(), ']'), line.end());
|
||
stringstream ss(line);
|
||
string token;
|
||
while (getline(ss, token, ',')) {
|
||
if (!token.empty()) {
|
||
result.push_back(stoi(token));
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return result;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// 格式化输出结果为字符串
|
||
string formatOutput(const vector<int>& res) {
|
||
if (res.empty()) return "[]";
|
||
stringstream ss;
|
||
ss << "[";
|
||
for (size_t i = 0; i < res.size(); ++i) {
|
||
ss << res[i];
|
||
if (i != res.size() - 1)
|
||
ss << ",";
|
||
}
|
||
ss << "]";
|
||
return ss.str();
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// Solution 类声明
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public:
|
||
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target);
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
int main() {
|
||
string line;
|
||
while (getline(cin, line)) {
|
||
vector<int> nums = parseIntArray(line);
|
||
|
||
if (!getline(cin, line)) break;
|
||
int target = stoi(line);
|
||
|
||
Solution sol;
|
||
vector<int> res = sol.twoSum(nums, target);
|
||
|
||
cout << formatOutput(res) << endl;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
return 0;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
vector<int> Solution::twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
|
||
|
||
return {};
|
||
}
|
||
`,
|
||
},
|
||
],
|
||
},
|
||
testcases: {
|
||
create: [
|
||
{
|
||
data: {
|
||
create: [
|
||
{ label: "nums", value: "[2,7,11,15]", index: 0 },
|
||
{ label: "target", value: "9", index: 1 },
|
||
],
|
||
},
|
||
expectedOutput: "[0,1]",
|
||
},
|
||
{
|
||
data: {
|
||
create: [
|
||
{ label: "nums", value: "[3,2,4]", index: 0 },
|
||
{ label: "target", value: "6", index: 1 },
|
||
],
|
||
},
|
||
expectedOutput: "[1,2]",
|
||
},
|
||
{
|
||
data: {
|
||
create: [
|
||
{ label: "nums", value: "[3,3]", index: 0 },
|
||
{ label: "target", value: "6", index: 1 },
|
||
],
|
||
},
|
||
expectedOutput: "[0,1]",
|
||
},
|
||
],
|
||
},
|
||
},
|
||
{
|
||
displayId: 1001,
|
||
title: "两数相加",
|
||
description: `给你两个 **非空** 的链表,表示两个非负的整数。它们每位数字都是按照 **逆序** 的方式存储的,并且每个节点只能存储 **一位** 数字。
|
||
|
||
请你将两个数相加,并以相同形式返回一个表示和的链表。
|
||
|
||
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数都不会以 0 开头。
|
||
|
||
### 示例 1:
|
||
|
||
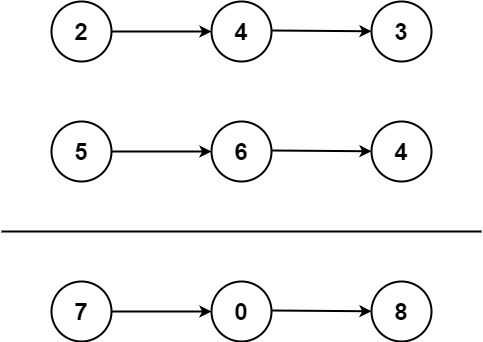
|
||
\`\`\`shell
|
||
输入:l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4]
|
||
输出:[7,0,8]
|
||
解释:342 + 465 = 807.
|
||
\`\`\`
|
||
|
||
### 示例 2:
|
||
|
||
\`\`\`shell
|
||
输入:l1 = [0], l2 = [0]
|
||
输出:[0]
|
||
\`\`\`
|
||
|
||
### 示例 3:
|
||
|
||
\`\`\`shell
|
||
输入:l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9]
|
||
输出:[8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]
|
||
\`\`\`
|
||
|
||
## 提示:
|
||
|
||
<div align="center">
|
||
每个链表中的节点数在范围 $[1, 100]$ 内
|
||
\`0 <= Node.val <= 9\`
|
||
题目数据保证列表表示的数字不含前导零
|
||
</div>
|
||
|
||
---
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
\`\`\`C++
|
||
\`\`\``,
|
||
solution: `## 方法一:模拟
|
||
|
||
### 思路与算法
|
||
|
||
由于输入的两个链表都是逆序存储数字的位数的,因此两个链表中同一位置的数字可以直接相加。
|
||
|
||
我们同时遍历两个链表,逐位计算它们的和,并与当前位置的进位值相加。具体而言,如果当前两个链表处相应位置的数字为 n1,n2,进位值为 carry,则它们的和为 n1+n2+carry;其中,答案链表处相应位置的数字为 (n1+n2+carry)mod10,而新的进位值为 ⌊
|
||
10
|
||
|
||
|
||
如果两个链表的长度不同,则可以认为长度短的链表的后面有若干个 $0$ 。
|
||
|
||
此外,如果链表遍历结束后,有 $carry>0$,还需要在答案链表的后面附加一个节点,节点的值为 carry。
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
### 代码
|
||
|
||
\`\`\`c showLineNumbers
|
||
struct ListNode* addTwoNumbers(struct ListNode* l1, struct ListNode* l2) {
|
||
struct ListNode* dummyHead = malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
|
||
dummyHead->val = 0;
|
||
dummyHead->next = NULL;
|
||
struct ListNode* curr = dummyHead;
|
||
int carry = 0;
|
||
|
||
while (l1 != NULL || l2 != NULL || carry != 0) {
|
||
int x = (l1 != NULL) ? l1->val : 0;
|
||
int y = (l2 != NULL) ? l2->val : 0;
|
||
int sum = carry + x + y;
|
||
carry = sum / 10;
|
||
|
||
curr->next = malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
|
||
curr->next->val = sum % 10;
|
||
curr->next->next = NULL;
|
||
curr = curr->next;
|
||
|
||
if (l1 != NULL) l1 = l1->next;
|
||
if (l2 != NULL) l2 = l2->next;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
struct ListNode* result = dummyHead->next;
|
||
free(dummyHead); // Free the memory allocated for dummyHead
|
||
return result;
|
||
}
|
||
\`\`\`
|
||
|
||
### 复杂度分析
|
||
|
||
- **时间复杂度:** $O(max(m,n))$
|
||
|
||
其中 $m$ 和 $n$ 分别为两个链表的长度。我们要遍历两个链表的全部位置,而处理每个位置只需要 $O(1)$ 的时间。
|
||
|
||
- **空间复杂度:** $O(1)$
|
||
|
||
注意返回值不计入空间复杂度。
|
||
|
||
`,
|
||
difficulty: "MEDIUM",
|
||
published: true,
|
||
templates: {
|
||
create: [
|
||
{
|
||
language: "c",
|
||
template: `
|
||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||
#include <string.h>
|
||
|
||
// Definition for singly-linked list.
|
||
struct ListNode {
|
||
int val;
|
||
struct ListNode *next;
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
// 创建链表
|
||
struct ListNode* createList(char *line) {
|
||
struct ListNode dummy;
|
||
struct ListNode *tail = &dummy;
|
||
dummy.next = NULL;
|
||
|
||
line[strcspn(line, "\\n")] = 0;
|
||
char *p = line;
|
||
while (*p && (*p == '[' || *p == ' ' || *p == ']')) p++;
|
||
|
||
char *token = strtok(p, ",");
|
||
while (token) {
|
||
struct ListNode *node = malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
|
||
node->val = atoi(token);
|
||
node->next = NULL;
|
||
tail->next = node;
|
||
tail = node;
|
||
token = strtok(NULL, ",");
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
return dummy.next;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// 打印链表
|
||
void printList(struct ListNode* head) {
|
||
printf("[");
|
||
while (head) {
|
||
printf("%d", head->val);
|
||
if (head->next) printf(",");
|
||
head = head->next;
|
||
}
|
||
printf("]\\n");
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// 释放链表内存
|
||
void freeList(struct ListNode* head) {
|
||
while (head) {
|
||
struct ListNode* temp = head;
|
||
head = head->next;
|
||
free(temp);
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// 主函数
|
||
int main() {
|
||
char line[1024];
|
||
|
||
while (fgets(line, sizeof(line), stdin)) {
|
||
struct ListNode* l1 = createList(line);
|
||
|
||
if (!fgets(line, sizeof(line), stdin)) break;
|
||
struct ListNode* l2 = createList(line);
|
||
|
||
struct ListNode* result = addTwoNumbers(l1, l2);
|
||
printList(result);
|
||
|
||
freeList(l1);
|
||
freeList(l2);
|
||
freeList(result);
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
return 0;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
|
||
struct ListNode* addTwoNumbers(struct ListNode* l1, struct ListNode* l2) {
|
||
|
||
return NULL; // 在这里填充你的算法逻辑
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
`,
|
||
},
|
||
{
|
||
language: "cpp",
|
||
template: `
|
||
#include <iostream>
|
||
#include <string>
|
||
#include <sstream>
|
||
#include <vector>
|
||
#include <algorithm>
|
||
using namespace std;
|
||
|
||
// Definition for singly-linked list.
|
||
struct ListNode {
|
||
int val;
|
||
ListNode *next;
|
||
ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
|
||
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
|
||
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
// 声明 Solution 类
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public:
|
||
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2);
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
// 输入字符串 -> 链表
|
||
ListNode* createList(const string& line) {
|
||
ListNode dummy;
|
||
ListNode* tail = &dummy;
|
||
dummy.next = nullptr;
|
||
|
||
string nums = line;
|
||
nums.erase(remove(nums.begin(), nums.end(), '['), nums.end());
|
||
nums.erase(remove(nums.begin(), nums.end(), ']'), nums.end());
|
||
|
||
stringstream ss(nums);
|
||
string token;
|
||
while (getline(ss, token, ',')) {
|
||
if (!token.empty()) {
|
||
int val = stoi(token);
|
||
tail->next = new ListNode(val);
|
||
tail = tail->next;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
return dummy.next;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// 打印链表
|
||
void printList(ListNode* head) {
|
||
cout << "[";
|
||
while (head) {
|
||
cout << head->val;
|
||
if (head->next) cout << ",";
|
||
head = head->next;
|
||
}
|
||
cout << "]" << endl;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// 释放内存
|
||
void freeList(ListNode* head) {
|
||
while (head) {
|
||
ListNode* tmp = head;
|
||
head = head->next;
|
||
delete tmp;
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
// 主函数
|
||
int main() {
|
||
string line;
|
||
while (getline(cin, line)) {
|
||
ListNode* l1 = createList(line);
|
||
if (!getline(cin, line)) break;
|
||
ListNode* l2 = createList(line);
|
||
|
||
Solution sol;
|
||
ListNode* res = sol.addTwoNumbers(l1, l2);
|
||
printList(res);
|
||
|
||
freeList(l1);
|
||
freeList(l2);
|
||
freeList(res);
|
||
}
|
||
return 0;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
|
||
ListNode* Solution::addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
|
||
|
||
return nullptr; // 在这里填充你的算法逻辑
|
||
}
|
||
`,
|
||
},
|
||
],
|
||
},
|
||
testcases: {
|
||
create: [
|
||
{
|
||
data: {
|
||
create: [
|
||
{ label: "l1", value: "[2,4,3]", index: 0 },
|
||
{ label: "l2", value: "[5,6,4]", index: 1 },
|
||
],
|
||
},
|
||
expectedOutput: "[7,0,8]",
|
||
},
|
||
{
|
||
data: {
|
||
create: [
|
||
{ label: "l1", value: "[0]", index: 0 },
|
||
{ label: "l2", value: "[0]", index: 1 },
|
||
],
|
||
},
|
||
expectedOutput: "[0]",
|
||
},
|
||
{
|
||
data: {
|
||
create: [
|
||
{ label: "l1", value: "[9,9,9,9,9,9,9]", index: 0 },
|
||
{ label: "l2", value: "[9,9,9,9]", index: 1 },
|
||
],
|
||
},
|
||
expectedOutput: "[8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]",
|
||
},
|
||
],
|
||
},
|
||
},
|
||
],
|
||
},
|
||
},
|
||
{
|
||
name: "fly6516",
|
||
email: "fly6516@outlook.com",
|
||
password: "$2b$10$SD1T/dYvKTArGdTmf8ERxuBKIONxY01/wSboRNaNsHnKZzDhps/0u",
|
||
role: "ADMIN",
|
||
problems: {
|
||
create: [
|
||
{
|
||
displayId: 1002,
|
||
title: "寻找两个正序数组的中位数",
|
||
description: `给定两个大小分别为 \`m\` 和 \`n\` 的正序(从小到大)数组 \`nums1\` 和 \`nums2\`。请你找出并返回这两个正序数组的 **中位数** 。
|
||
|
||
算法的时间复杂度应该为 \`O(log (m+n))\` 。
|
||
|
||
### 示例 1:
|
||
|
||
\`\`\`shell
|
||
输入:nums1 = [1,3], nums2 = [2]
|
||
输出:2.00000
|
||
解释:合并数组 = [1,2,3] ,中位数 2
|
||
\`\`\`
|
||
|
||
### 示例 2:
|
||
|
||
\`\`\`shell
|
||
输入:nums1 = [1,2], nums2 = [3,4]
|
||
输出:2.50000
|
||
解释:合并数组 = [1,2,3,4] ,中位数 (2 + 3) / 2 = 2.5
|
||
\`\`\`
|
||
|
||
## 提示:
|
||
|
||
\`\`\`math
|
||
nums1.length == m
|
||
\`\`\`
|
||
\`\`\`math
|
||
nums2.length == n
|
||
\`\`\`
|
||
\`\`\`math
|
||
0 <= m <= 1000
|
||
\`\`\`
|
||
\`\`\`math
|
||
0 <= n <= 1000
|
||
\`\`\`
|
||
\`\`\`math
|
||
1 <= m + n <= 2000
|
||
\`\`\`
|
||
\`\`\`math
|
||
-10^6 <= nums1[i], nums2[i] <= 10^6
|
||
\`\`\`
|
||
|
||
---
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
\`\`\`C++
|
||
\`\`\``,
|
||
solution: `## 方法一:归并排序
|
||
|
||
### 思路
|
||
|
||
让我们从最直接的方法开始。如果我们将两个数组的元素放入一个数组 \`A\` 并进行排序。假设合并后的数组长度为 \`n\`,那么中位数是:
|
||
|
||
- 如果 \`n\` 是奇数,则为 \`A[n / 2]\`。
|
||
|
||
- 如果 \`n\` 是偶数,则为 \`A[n / 2]\` 和 \`A[n / 2 + 1]\` 的平均值。
|
||
|
||
然而,我们其实并不需要真的合并并排序这些数组。注意两个数组已经排好序了,所以最小的元素要么是 \`nums1\` 的第一个元素,要么是 \`nums2\` 的第一个元素。因此,我们可以将两个指针 \`p1\` 和 \`p2\` 分别放在每个数组的开头,然后我们可以通过比较 \`nums1[p1]\` 和 \`nums2[p2]\` 的值来获取最小的元素。
|
||
|
||
请参考以下幻灯片作为示例:
|
||
|
||
### 算法
|
||
|
||
1. 获取两个数组的总长度 \`m + n\`
|
||
|
||
- 如果 \`m + n\` 是奇数,我们寻找第 \`(m + n) / 2\` 个元素。
|
||
|
||
- 如果 \`m + n\` 是偶数,我们寻找第 \`(m + n) / 2\` 和第 \`(m + n) / 2 + 1\` 个元素的平均值。
|
||
|
||
2. 将两个指针 \`p1\` 和 \`p2\` 分别放在数组 \`nums1\` 和 \`nums2\` 的开头。
|
||
|
||
3. 如果 \`p1\` 和 \`p2\` 都在数组范围内,比较 \`p1\` 和 \`p2\` 处的值:
|
||
|
||
- 如果 \`nums1[p1]\` 小于 \`nums2[p2]\`,则将 \`p1\` 向右移动一位。
|
||
|
||
- 否则,将 \`p2\` 向右移动一位。
|
||
|
||
如果 \`p1\` 超出了 \`nums1\` 的范围,就将 \`p2\` 向右移动一位。
|
||
|
||
如果 \`p2\` 超出了 \`nums2\` 的范围,就将 \`p1\` 向右移动一位。
|
||
|
||
4. 获取目标元素并计算中位数:
|
||
|
||
- 如果 \`m + n\` 是奇数,重复第 3 步 \`(m + n + 1) / 2\` 次并返回最后一个元素。
|
||
|
||
- 如果 \`m + n\` 是偶数,重复第 3 步 \`(m + n) / 2 + 1\` 次并返回最后两个元素的平均值。
|
||
|
||
### 实现
|
||
|
||
\`\`\`c showLineNumbers
|
||
double findMedianSortedArrays(int* nums1, int nums1Size, int* nums2, int nums2Size) {
|
||
int m = nums1Size, n = nums2Size;
|
||
int p1 = 0, p2 = 0;
|
||
|
||
int getMin() {
|
||
if (p1 < m && p2 < n) {
|
||
return nums1[p1] < nums2[p2] ? nums1[p1++] : nums2[p2++];
|
||
} else if (p1 < m) {
|
||
return nums1[p1++];
|
||
} else if (p2 < n) {
|
||
return nums2[p2++];
|
||
}
|
||
return -1;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
double median;
|
||
if ((m + n) % 2 == 0) {
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < ((m + n) / 2) - 1; ++i) {
|
||
int temp = getMin();
|
||
}
|
||
median = (getMin() + getMin()) / 2.0;
|
||
} else {
|
||
for (int i = 0; i < (m + n) / 2; ++i) {
|
||
int temp = getMin();
|
||
}
|
||
median = getMin();
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
return median;
|
||
}
|
||
\`\`\`
|
||
|
||
### 复杂度分析
|
||
|
||
令 $m$ 为数组 \`nums1\` 的大小,$n$ 为数组 \`nums2\` 的大小。
|
||
|
||
- **时间复杂度:** $O(m + n)$
|
||
|
||
- 我们通过比较 \`p1\` 和 \`p2\` 处的两个值来获取最小元素,比较两个元素并移动相应指针耗时 $O(1)$。
|
||
|
||
- 在到达中位数元素之前,我们需要遍历数组的一半。
|
||
|
||
- 总的来说,时间复杂度为 $O(m + n)$。
|
||
|
||
- **空间复杂度:** $O(1)$
|
||
|
||
- 我们只需要保持两个指针 \`p1\` 和 \`p2\`。
|
||
|
||
`,
|
||
difficulty: "HARD",
|
||
published: true,
|
||
templates: {
|
||
create: [
|
||
{
|
||
language: "c",
|
||
template: `
|
||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||
#include <string.h>
|
||
|
||
// 解析输入数组
|
||
int *parseIntArray(char *line, int *len) {
|
||
line[strcspn(line, "\\n")] = 0; // 移除换行符
|
||
char *p = line;
|
||
while (*p && (*p == '[' || *p == ' ' || *p == ']')) p++; // 跳过空格和括号
|
||
|
||
int capacity = 10;
|
||
int *arr = malloc(capacity * sizeof(int)); // 初始分配空间
|
||
*len = 0;
|
||
|
||
char *token = strtok(p, ","); // 分割输入为逗号分隔的整数
|
||
while (token) {
|
||
if (*len >= capacity) { // 扩展数组大小
|
||
capacity *= 2;
|
||
arr = realloc(arr, capacity * sizeof(int));
|
||
}
|
||
arr[(*len)++] = atoi(token); // 存储整数
|
||
token = strtok(NULL, ",");
|
||
}
|
||
return arr;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
double findMedianSortedArrays(int* nums1, int nums1Size, int* nums2, int nums2Size);
|
||
|
||
int main() {
|
||
char line[1024];
|
||
|
||
while (fgets(line, sizeof(line), stdin)) { // 读取第一行
|
||
int len1;
|
||
int *nums1 = parseIntArray(line, &len1); // 解析数组1
|
||
|
||
if (!fgets(line, sizeof(line), stdin)) break; // 如果第二行不存在,退出
|
||
int len2;
|
||
int *nums2 = parseIntArray(line, &len2); // 解析数组2
|
||
|
||
double result = findMedianSortedArrays(nums1, len1, nums2, len2); // 计算中位数
|
||
printf("%.5f\\n", result); // 输出中位数,保留5位小数
|
||
|
||
free(nums1); // 释放内存
|
||
free(nums2); // 释放内存
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
return 0;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
|
||
// 寻找中位数函数
|
||
double findMedianSortedArrays(int* nums1, int nums1Size, int* nums2, int nums2Size) {
|
||
|
||
return 0.0; // 在这里填充你的算法逻辑
|
||
}
|
||
`,
|
||
},
|
||
{
|
||
language: "cpp",
|
||
template: `
|
||
#include <iostream>
|
||
#include <vector>
|
||
#include <string>
|
||
#include <sstream>
|
||
#include <algorithm>
|
||
using namespace std;
|
||
|
||
class Solution {
|
||
public:
|
||
double findMedianSortedArrays(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2);
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
// 解析输入为整数数组
|
||
vector<int> parseIntArray(const string& line) {
|
||
string trimmed = line;
|
||
trimmed.erase(remove(trimmed.begin(), trimmed.end(), '['), trimmed.end());
|
||
trimmed.erase(remove(trimmed.begin(), trimmed.end(), ']'), trimmed.end());
|
||
|
||
vector<int> result;
|
||
stringstream ss(trimmed);
|
||
string token;
|
||
while (getline(ss, token, ',')) {
|
||
if (!token.empty()) {
|
||
result.push_back(stoi(token));
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
return result;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
int main() {
|
||
string line;
|
||
while (getline(cin, line)) {
|
||
vector<int> nums1 = parseIntArray(line);
|
||
if (!getline(cin, line)) break;
|
||
vector<int> nums2 = parseIntArray(line);
|
||
|
||
Solution sol;
|
||
double result = sol.findMedianSortedArrays(nums1, nums2);
|
||
printf("%.5f\\n", result);
|
||
}
|
||
return 0;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
double Solution::findMedianSortedArrays(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
|
||
|
||
return 0.0; // 临时返回值,待填充
|
||
}
|
||
`,
|
||
},
|
||
],
|
||
},
|
||
testcases: {
|
||
create: [
|
||
{
|
||
data: {
|
||
create: [
|
||
{ label: "nums1", value: "[1,3]", index: 0 },
|
||
{ label: "nums2", value: "[2]", index: 1 },
|
||
],
|
||
},
|
||
expectedOutput: "2.00000",
|
||
},
|
||
{
|
||
data: {
|
||
create: [
|
||
{ label: "nums1", value: "[1,2]", index: 0 },
|
||
{ label: "nums2", value: "[3,4]", index: 1 },
|
||
],
|
||
},
|
||
expectedOutput: "2.50000",
|
||
},
|
||
],
|
||
},
|
||
},
|
||
],
|
||
},
|
||
},
|
||
];
|
||
|
||
export async function main() {
|
||
for (const e of editorLanguageConfigData) {
|
||
await prisma.editorLanguageConfig.create({ data: e });
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
for (const u of userData) {
|
||
await prisma.user.create({ data: u });
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
main();
|